Slack Integration Guide
Overview
The Slack integration allows your NINA workflows to connect with Slack for messaging, channel management, and team collaboration. This integration enables you to send and manage messages, create and interact with channels, retrieve user information, search content, and manage reminders, all directly from your workflows.
Status
At present, our integration comprehensively supports key functionalities related to messaging, channel operations, user information, content search, and reminders. However, there are still several areas not covered by this integration, mainly:
- Apps: Management and interaction with Slack apps.
- Files: Handling of file uploads and downloads.
- Teams: Management of team settings and information.
- Views: Configuration and management of Slack views and modals.
Credential Configuration
Before using the Slack integration in your workflows, you need to configure credentials for authentication. The NINA platform supports two authentication methods for Slack:
Authentication Methods
1. API Token Authentication
The simplest method is to use a Slack API token:
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| API Token | Slack API token for authentication | xoxb-1234567890-1234567890123-abc123def456ghi789jkl |
| Auth Type | Authentication type | apiToken |
How to get your API Token:
- Go to the Slack API website
- Create a new Slack app (or select an existing one)
- Navigate to "OAuth & Permissions" in the sidebar
- Add the required scopes based on the functionality you need:
chat:write- For sending messageschannels:read- For reading channel informationchannels:write- For creating or modifying channelsusers:read- For retrieving user informationsearch:read- For searching messages and filesreminders:write- For creating remindersreminders:read- For retrieving reminders
- Install the app to your workspace
- Copy the "Bot User OAuth Token" that starts with
xoxb-
2. OAuth2 Authentication
For more advanced scenarios or when you need to interact with multiple workspaces, you can use OAuth2 authentication:
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Client ID | OAuth2 client ID | 1234567890.1234567890 |
| Client Secret | OAuth2 client secret | abc123def456ghi789jkl |
| Access Token | OAuth2 access token | xoxp-1234567890-1234567890123-abc123def456ghi789jkl |
| Auth URL | Authorization URL | https://slack.com/oauth/v2/authorize |
| Access Token URL | Access token URL | https://slack.com/api/oauth.v2.access |
| Scope | OAuth2 scopes | chat:write,channels:read,channels:write,users:read,search:read,reminders:write,reminders:read |
| Auth Type | Authentication type | oauth2 |
How to set up OAuth2:
- Go to the Slack API website
- Create a new Slack app (or select an existing one)
- Navigate to "OAuth & Permissions" in the sidebar
- Add the required scopes
- Add redirect URLs (the callback URL from your NINA instance)
- For POC environment:
https://poc.zynap.com/api/v1/oauth2/callback - For Production environment:
https://platform.zynap.com/api/v1/oauth2/callback
- For POC environment:
- Install the app to your workspace
- Note your Client ID, Client Secret, and Access Token
Creating a Slack Credential
-
Navigate to the Credentials section in NINA
-
Click Add New Credential
-
Fill in the credential details:
- Name: A descriptive name (e.g., "Slack Production")
- Description: Optional details about the credential's purpose
- Integration Service: Select "Slack"
- Auth Type: Choose "apiToken" or "oauth2"
- Fill in the authentication fields based on your selected auth type
-
Click Test Connection to verify credentials
-
Click Save to store the credential
Supported Resources and Operations
The Slack integration supports the following resources and operations:
Message
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Post | Sends a message to a Slack channel |
| Update | Updates an existing message |
| Delete | Deletes a message |
Channel
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Create | Creates a new channel |
| Get | Gets information about a channel |
| Get All | Gets a list of all channels |
| Archive | Archives a channel |
| Unarchive | Unarchives a channel |
| Join | Joins a channel |
| Leave | Leaves a channel |
| History | Gets message history for a channel |
User
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Get | Gets information about a user |
| Get All | Gets a list of all users |
| Get Profile | Gets a user's profile information |
Search
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Messages | Searches for messages matching a query |
| Files | Searches for files matching a query |
Reminder
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Create | Creates a new reminder |
| Get | Gets information about a reminder |
| Get All | Gets a list of all reminders |
| Delete | Deletes a reminder |
| Complete | Marks a reminder as complete |
File
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Upload | Uploads a file to Slack |
| Get | Gets information about a file |
| Get All | Gets a list of all files |
Parameter Merging
The Slack integration takes full advantage of NINA's parameter merging capabilities:
Parameter Sources (in order of precedence)
- Node Parameters: Parameters configured directly in the Slack Integration Node
- Extracted Parameters: Parameters automatically extracted from the input data
- Input Data: The complete input data from upstream nodes
When a Slack Integration Node executes:
- It combines parameters from all sources
- Node parameters take precedence over extracted parameters
- The combined parameters are used to execute the Slack operation
Example: Sending Messages
Basic Message Posting
Below is an example of posting a message to a Slack channel:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "message",
"operation": "post",
"parameters": {
"channel": {
"mode": "id",
"value": "C012345678"
},
"text": "Alert: Security vulnerability detected in production environment",
"additionalFields": {
"username": "Security Bot",
"iconEmoji": ":shield:"
}
}
}
Message with Custom Formatting
You can use Slack's rich formatting to create more engaging messages:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "message",
"operation": "post",
"parameters": {
"channel": {
"mode": "name",
"value": "security-alerts"
},
"text": "Alert: Critical vulnerability detected",
"additionalFields": {
"blocks": "[{\"type\":\"header\",\"text\":{\"type\":\"plain_text\",\"text\":\"Security Alert: Critical Vulnerability\",\"emoji\":true}},{\"type\":\"section\",\"text\":{\"type\":\"mrkdwn\",\"text\":\"*Severity:* Critical\\n*Component:* Authentication Service\\n*Status:* Investigation in progress\"}},{\"type\":\"section\",\"text\":{\"type\":\"mrkdwn\",\"text\":\"The authentication service is experiencing unusual login patterns that may indicate a brute force attack.\"}},{\"type\":\"actions\",\"elements\":[{\"type\":\"button\",\"text\":{\"type\":\"plain_text\",\"text\":\"View Details\",\"emoji\":true},\"style\":\"primary\",\"value\":\"view_details\"},{\"type\":\"button\",\"text\":{\"type\":\"plain_text\",\"text\":\"Acknowledge\",\"emoji\":true},\"value\":\"acknowledge\"}]}]"
}
}
}
Updating a Message
Update an existing message in a Slack channel:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "message",
"operation": "update",
"parameters": {
"channel": {
"mode": "id",
"value": "C012345678"
},
"ts": "1234567890.123456",
"text": "Alert: Security vulnerability investigation completed - No threat found",
"additionalFields": {
"blocks": "[{\"type\":\"header\",\"text\":{\"type\":\"plain_text\",\"text\":\"Security Alert: RESOLVED\",\"emoji\":true}},{\"type\":\"section\",\"text\":{\"type\":\"mrkdwn\",\"text\":\"*Severity:* Resolved\\n*Component:* Authentication Service\\n*Status:* Investigation completed\"}},{\"type\":\"section\",\"text\":{\"type\":\"mrkdwn\",\"text\":\"The suspicious login patterns have been analyzed and determined to be legitimate traffic. No further action required.\"}}]"
}
}
}
Deleting a Message
Delete a message from a Slack channel:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "message",
"operation": "delete",
"parameters": {
"channel": {
"mode": "id",
"value": "C012345678"
},
"ts": "1234567890.123456"
}
}
Example: Channel Operations
Creating a Channel
Create a new Slack channel:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "channel",
"operation": "create",
"parameters": {
"name": "incident-response",
"additionalFields": {
"isPrivate": true
}
}
}
Getting Channel Information
Retrieve information about a specific channel:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "channel",
"operation": "get",
"parameters": {
"channel": {
"mode": "name",
"value": "general"
}
}
}
Getting Channel History
Retrieve message history for a channel:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "channel",
"operation": "history",
"parameters": {
"channel": {
"mode": "id",
"value": "C012345678"
},
"limit": 50,
"additionalFields": {
"oldest": "1234567890.123456",
"latest": "1234567899.123456"
}
}
}
Example: User Operations
Getting User Information
Retrieve information about a specific user:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "user",
"operation": "get",
"parameters": {
"user": {
"mode": "id",
"value": "U012345678"
}
}
}
Getting All Users
Retrieve a list of all users in the workspace:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "user",
"operation": "getAll",
"parameters": {
"returnAll": true
}
}
Example: Search Operations
Searching Messages
Search for messages in a workspace:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "search",
"operation": "messages",
"parameters": {
"query": "security vulnerability",
"returnAll": false,
"limit": 50,
"additionalFields": {
"sort": "timestamp",
"sortDirection": "desc",
"highlight": true
}
}
}
Example: Reminder Operations
Creating a Reminder
Create a new reminder:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "reminder",
"operation": "create",
"parameters": {
"text": "Review security incident report",
"time": "tomorrow at 10am",
"additionalFields": {
"user": {
"mode": "id",
"value": "U012345678"
}
}
}
}
Getting All Reminders
Retrieve a list of all reminders:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "reminder",
"operation": "getAll",
"parameters": {}
}
Integration in Workflow Context
The Slack integration is particularly powerful when combined with other nodes in a workflow:
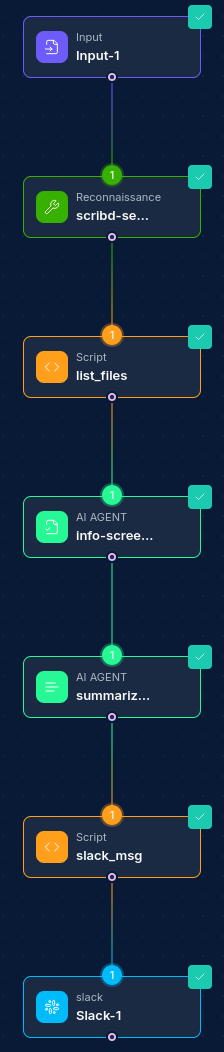
Common Workflow Patterns:
-
Security Alert Notification:
- Security Scanner Node → Script Node (process results) → Slack Integration Node (post message) → Database Node (log notification)
-
Incident Response Coordination:
- Webhook Node (receive alert) → Script Node (triage) → Slack Integration Node (create channel) → Slack Integration Node (post initial report) → Task Assignment Node
-
Automated Status Updates:
- Schedule Node → Database Node (get status) → Script Node (format data) → Slack Integration Node (post message)
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Resolution |
|---|---|
| Authentication failures | Verify your API token or OAuth credentials are correct and have not expired. Ensure your token has the necessary scopes for the operations you're trying to perform. |
| Channel not found | Check that the channel name or ID is correct. Verify that the channel exists and is accessible to the authenticated bot user. For private channels, ensure your bot has been invited to the channel. |
| Rate limiting | Slack has rate limits on API calls. If you're hitting these limits, consider adding delays between operations. Monitor the HTTP 429 responses and implement exponential backoff for retries. |
| Message formatting errors | When using Block Kit for message formatting, validate your JSON syntax. Use a tool like Block Kit Builder to test your message formatting before implementing in a workflow. |
| Permission errors | Ensure your app has the required OAuth scopes for the operations you're trying to perform. Different operations require different permissions. |
| Ephemeral message errors | When sending ephemeral messages (visible only to one user), ensure you're providing a valid user ID with the message. |
| File upload limitations | Be aware of file size limits when uploading files. Slack typically limits file uploads to 1GB for paid workspaces and 50MB for free workspaces. |
Best Practices
-
Use Resource Locators: When working with channels and users, use resource locators to select from available options rather than entering IDs directly.
-
Leverage Block Kit: For rich, interactive messages, use Slack's Block Kit rather than simple text messages. Block Kit provides more control over formatting and allows for interactive elements.
-
Be Mindful of Rate Limits: Slack imposes rate limits on API calls. Design workflows to respect these limits and implement proper handling for rate limit errors.
-
Use Meaningful Bot Names and Icons: Customize your bot's appearance using custom names and icons to make messages more engaging and clear about their source.
-
Secure Your Tokens: Keep your Slack API tokens and OAuth credentials secure. Use the system's built-in credential management rather than hardcoding values.
-
Handle Errors Gracefully: Implement proper error handling in your workflows to gracefully handle failed Slack API calls.
-
Use Threads for Related Messages: For workflows that generate multiple related messages, consider using thread replies to keep conversations organized.
-
Test with Limited Audience: When testing new workflows, consider using private channels or direct messages to limit the audience until you're confident in the integration.
-
Document Message Formats: Keep a record of your message formats, especially complex Block Kit payloads, for easier maintenance and updates.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitor your Slack integrations to ensure they're functioning correctly and not encountering rate limits or other issues.