MongoDB Integration Guide
Overview
The MongoDB integration allows your NINA workflows to connect with MongoDB databases for document management and querying. This integration enables you to find, insert, update, and delete documents, as well as perform aggregation operations directly from your workflows.
Status
The integration currently supports all core MongoDB collection operations including finding, inserting, updating, and deleting documents. It also supports more advanced operations like aggregation pipelines and atomic operations such as findOneAndUpdate.
Some of the main features we do not yet support include:
- Database Administration: Creating or dropping databases and collections
- Index Management: Creating, managing, or dropping indexes
- User Management: Creating or managing database users and roles
- Transactions: Multi-document transactions across collections
- Change Streams: Watching for changes in the database
- GridFS: Storing and retrieving large files
Credential Configuration
Before using the MongoDB integration in your workflows, you need to configure credentials for authentication. The NINA platform supports authentication via connection string or individual connection parameters.
Authentication Methods
Connection String
You can provide a complete MongoDB connection string:
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Connection String | MongoDB URI | mongodb+srv://username:[email protected] |
| Database | Database name (can override the one in URI) | myDatabase |
Connection String Formats:
mongodb+srv://username:[email protected]
mongodb://username:password@hostname:port/database?authSource=admin
Common Connection String Options:
authSource=admin: Specifies the authentication databaseretryWrites=true: Enables retryable writesw=majority: Sets write concern to majorityssl=true: Enables SSL connectionreplicaSet=myReplicaSet: Specifies replica set name
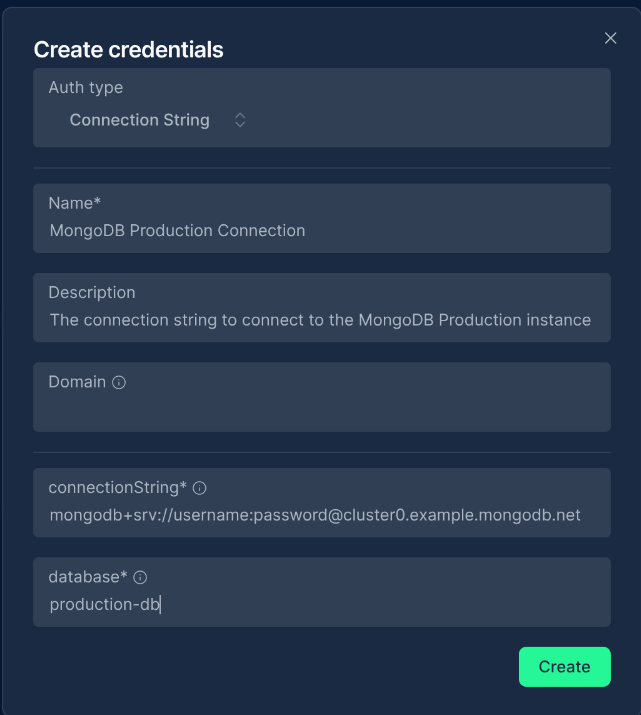
Connection Parameters
Alternatively, you can provide individual connection parameters:
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Host | MongoDB server hostname | mongodb.example.com or localhost |
| Port | MongoDB server port | 27017 |
| Database | Database name | myDatabase |
| Username | Username for authentication | dbuser |
| Password | Password for authentication | password123 |
| Auth Source | Authentication database | admin |
Creating a MongoDB Credential
-
Navigate to the Credentials section in NINA
-
Click Add New Credential
-
Fill in the credential details:
- Name: A descriptive name (e.g., "MongoDB Production")
- Description: Optional details about the credential's purpose
- Integration Service: Select "MongoDB"
- Fill in either the connection string or the individual connection parameters
-
Click Test Connection to verify credentials
-
Click Save to store the credential
Supported Resources and Operations
The MongoDB integration supports the following resources and operations:
Collection
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| find | Finds documents in a collection based on a query |
| insert | Inserts one or more documents into a collection |
| update | Updates documents in a collection |
| findOneAndUpdate | Finds and updates a single document atomically |
| findOneAndReplace | Finds and replaces a single document atomically |
| delete | Deletes documents from a collection |
| aggregate | Performs aggregation operations on a collection |
Parameter Merging
The MongoDB integration takes full advantage of NINA's parameter merging capabilities:
Parameter Sources (in order of precedence)
- Node Parameters: Parameters configured directly in the MongoDB Integration Node
- Extracted Parameters: Parameters automatically extracted from the input data
- Input Data: The complete input data from upstream nodes
When a MongoDB Integration Node executes:
- It combines parameters from all sources
- Node parameters take precedence over extracted parameters
- The combined parameters are used to execute the MongoDB operation
Example: Finding Documents
Basic Document Query
Below is an example of finding documents in a MongoDB collection:
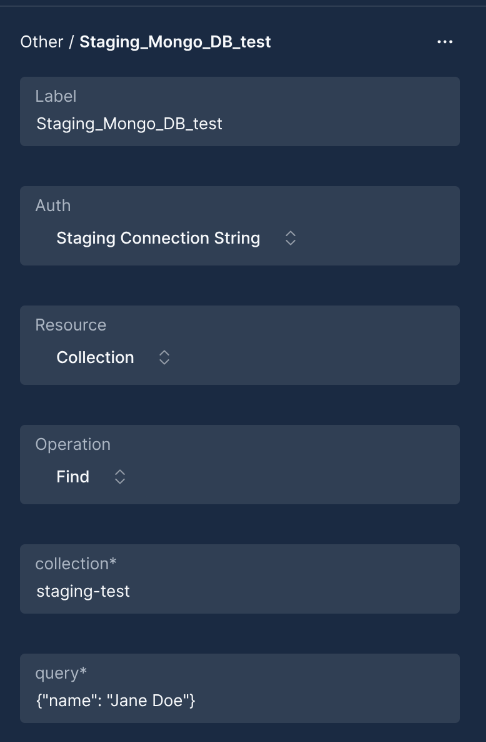
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "collection",
"operation": "find",
"parameters": {
"collection": "users",
"query": {"status": "active", "age": {"$gt": 21}},
"options": {
"limit": 10,
"sort": {"lastLogin": -1},
"projection": {"_id": 1, "name": 1, "email": 1}
}
}
}
Document Insertion
Example of inserting documents into a MongoDB collection:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "collection",
"operation": "insert",
"parameters": {
"collection": "alerts",
"inputData": {
"severity": "high",
"source": "firewall",
"message": "Unauthorized access attempt detected",
"timestamp": "2024-05-15T10:30:00Z",
"details": {
"sourceIP": "192.168.1.100",
"destinationIP": "10.0.0.5",
"port": 22
}
},
"options": {
"dateFields": "timestamp"
}
}
}
Document Update
Example of updating documents in a MongoDB collection:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "collection",
"operation": "update",
"parameters": {
"collection": "incidents",
"updateKey": "_id",
"inputData": {
"_id": "6078c15e1b5c2a001f9e6a7b",
"status": "resolved",
"resolvedAt": "2024-05-15T15:45:00Z",
"resolvedBy": "user123"
},
"fields": "status,resolvedAt,resolvedBy",
"options": {
"dateFields": "resolvedAt"
}
}
}
Aggregation Pipeline
Example of running an aggregation pipeline on a MongoDB collection:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "collection",
"operation": "aggregate",
"parameters": {
"collection": "transactions",
"query": [
{"$match": {"status": "completed", "date": {"$gte": {"$date": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z"}}}},
{"$group": {"_id": "$category", "totalAmount": {"$sum": "$amount"}}},
{"$sort": {"totalAmount": -1}}
]
}
}
Advanced Features
Date Field Processing
The MongoDB integration automatically processes date fields if specified:
{
"options": {
"dateFields": "createdAt,updatedAt"
}
}
This will convert string date values to proper MongoDB Date objects.
Dot Notation Support
For nested fields, you can enable dot notation processing:
{
"options": {
"useDotNotation": true
}
}
This will flatten nested objects into dot notation format, which is useful for certain update operations.
Field Filtering
You can specify which fields to include in update operations:
{
"fields": "name,email,address.city"
}
Upsert Support
The integration supports upsert operations (insert if not exists, update if exists):
{
"upsert": true
}
Tips and Best Practices
-
Security: Always restrict your MongoDB user permissions to only what's necessary for your workflows.
-
Query Optimization: Use indexes for frequently queried fields to improve performance.
-
Date Handling: Use the
dateFieldsoption to ensure proper date handling between your workflow and MongoDB. -
Error Handling: Set up error handling in your workflow to catch and respond to MongoDB errors.
-
Input Validation: Validate input data before passing it to MongoDB operations to prevent errors.
-
Batch Operations: For large data sets, use batch operations and pagination to avoid memory issues.
-
Connection Management: The integration handles connection pooling automatically, but be mindful of concurrent operations.
-
Complex Queries: For complex queries, use the aggregation pipeline instead of simple find operations.
Troubleshooting
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Solution |
|---|---|
| Connection timeout | Check network connectivity, firewall settings, and that the MongoDB server is running |
| Authentication failed | Verify username, password, and authentication database |
| Document not found | Confirm the query criteria and collection name |
| Validation error | Ensure required fields are provided and have the correct data types |
| Cursor timeout | For long-running operations, consider using a different approach or adding limits |
Support
If you encounter issues with the MongoDB integration, please contact our support team for assistance.