OpenCTI Integration Guide
Overview
The OpenCTI integration allows your NINA workflows to connect with the OpenCTI threat intelligence platform. This integration enables you to search and retrieve threat intelligence data from your OpenCTI instance, helping you incorporate valuable threat intelligence into your security workflows.
OpenCTI (Open Cyber Threat Intelligence) is an open-source platform designed to store, organize, visualize, and share knowledge about cyber threats. The NINA integration provides a streamlined way to leverage this intelligence in your automated workflows.
Status
Currently, the only operation we support is searching observables.
Our integration does not yet support several key domains of the OpenCTI API, including but not limited to:
- Threat Actors: Information and management of entities responsible for malicious activities.
- Campaigns: Data related to coordinated threat activities over a period of time.
- Attack Patterns: Details on MITRE ATT&CK techniques and tactics used by adversaries.
- Courses of Action: Information on defensive measures and mitigations against threats.
- Identities: Data about organizations, individuals, sectors, or systems involved in or targeted by threats.
- Indicators: Specific patterns or observables indicating potential threats beyond basic searching.
- Infrastructures: Information on physical or virtual assets used by threat actors.
- Intrusion Sets: Grouped activities or behaviors associated with specific threat actors.
- Locations: Geographic data related to threats, such as regions, countries, or cities.
- STIX Bundle Operations: Full import/export capabilities for STIX 2.1 bundles.
- Workflow Integration: Setting workflow contexts or managing playbook integrations.
For a comprehensive list of OpenCTI capabilities, refer to the official Python client documentation (pycti) which can be found in the provided context or at the official OpenCTI resources.
Credential Configuration
Before using the OpenCTI integration in your workflows, you need to configure credentials for authentication.
Authentication Method
The OpenCTI integration uses API Key authentication:
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Base URL | OpenCTI platform URL | https://opencti.example.com |
| API Key | API key for authentication | a1b2c3d4-e5f6-g7h8-i9j0-k1l2m3n4o5p6 |
| Auth Type | Authentication type | apiKey |
How to get your API Key:
- Log in to your OpenCTI instance
- Go to your profile settings (typically in the upper right corner)
- Navigate to the API section
- Generate a new API key
- Copy the generated key
Creating an OpenCTI Credential
-
Navigate to the Credentials section in NINA
-
Click Add New Credential
-
Fill in the credential details:
- Name: A descriptive name (e.g., "OpenCTI Production")
- Description: Optional details about the credential's purpose
- Integration Service: Select "OpenCTI"
- Auth Type: "API Key" (this should be automatically selected)
- Base URL: Enter your OpenCTI instance URL
- API Key: Enter your OpenCTI API key
-
Click Test Connection to verify credentials
-
Click Save to store the credential
Supported Resources and Operations
The OpenCTI integration currently supports the following resources and operations:
Observable
Observables in OpenCTI represent indicators and observables of compromise (IOCs) such as IP addresses, domains, file hashes, etc.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Search | Searches for observables based on search criteria |
Parameter Merging
The OpenCTI integration takes advantage of NINA's parameter merging capabilities:
Parameter Sources (in order of precedence)
- Node Parameters: Parameters configured directly in the OpenCTI Integration Node
- Extracted Parameters: Parameters automatically extracted from the input data
- Input Data: The complete input data from upstream nodes
When an OpenCTI Integration Node executes:
- It combines parameters from all sources
- Node parameters take precedence over extracted parameters
- The combined parameters are used to execute the OpenCTI operation
Example: Searching Observables
The primary operation in the OpenCTI integration is searching for observables (indicators of compromise) based on search criteria.
Basic Observable Search
Below is an example of searching for observables in OpenCTI:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "observable",
"operation": "search",
"parameters": {
"searchParams": ["ransomware", "emotet"],
"count": 50
}
}
This will search for observables related to both "ransomware" and "emotet" and return up to 50 results.
Searching for Specific IOC Types
You can search for specific types of indicators by including the type in your search parameters:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "observable",
"operation": "search",
"parameters": {
"searchParams": ["IP", "185.159.83.24"],
"count": 10
}
}
This will search for observables related to the specific IP address "185.159.83.24".
Searching for Multiple Terms
You can combine multiple search terms to narrow down your results:
Node Configuration:
{
"resource": "observable",
"operation": "search",
"parameters": {
"searchParams": ["APT28", "domain", "C2"],
"count": 25
}
}
This will search for domain observables related to APT28 command and control servers.
Integration in Workflow Context
The OpenCTI integration is particularly powerful when combined with other nodes in a workflow:
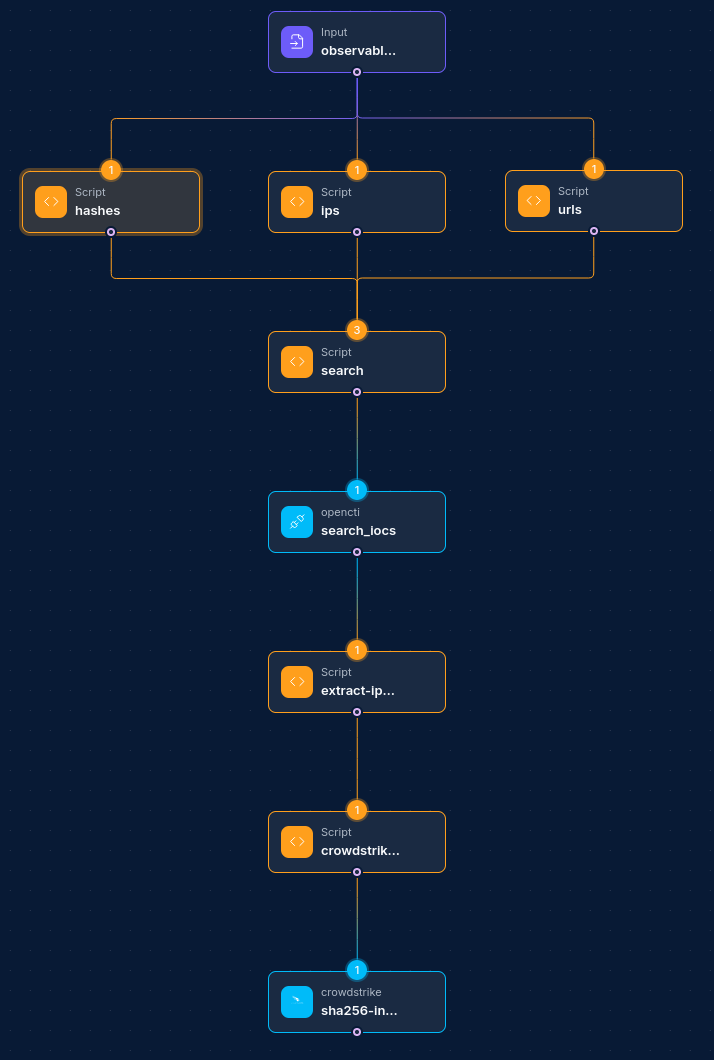
Common Workflow Patterns:
-
Threat Intelligence Enrichment:
- Input Node (receives IOC) → OpenCTI Integration Node (search) → Script Node (process results) → Report Node (generate enriched report)
-
Alert Triage Pipeline:
- Security Alert Node → Script Node (extract indicators) → OpenCTI Integration Node (search) → Script Node (evaluate threat score) → Slack Integration Node (notify team)
-
Malware Analysis Enrichment:
- Malware Analysis Node → Script Node (extract IOCs) → OpenCTI Integration Node (search) → Database Node (store enriched results)
-
Threat Hunting:
- Schedule Node → Database Node (get hunting rules) → OpenCTI Integration Node (search) → Script Node (filter/analyze) → SIEM Integration Node
Search Response Structure
When you execute a search operation, the response will be structured according to the OpenCTI GraphQL API. Here's a simplified example of what the response structure might look like:
{
"data": {
"globalSearch": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"id": "indicator--a1b2c3d4-e5f6-g7h8-i9j0-k1l2m3n4o5p6",
"entity_type": "Indicator",
"created_at": "2023-08-15T14:22:13.000Z",
"representative": {
"main": "185.159.83.24",
"secondary": "IP Address"
},
"objectLabel": [
{
"id": "label--a1b2c3d4-e5f6-g7h8-i9j0-k1l2m3n4o5p6",
"value": "malicious-ip",
"color": "#FF5722"
}
]
},
"cursor": "YXJyYXljb25uZWN0aW9uOjA="
}
],
"pageInfo": {
"endCursor": "YXJyYXljb25uZWN0aW9uOjI0",
"hasNextPage": true,
"globalCount": 156
}
}
}
}
You can use a Script Node to process and extract the relevant information from this response structure.
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Resolution |
|---|---|
| Authentication failures | Verify your API key is correct and has not expired. Ensure that your base URL is correctly formatted and includes the protocol (https://). |
| Empty search results | Check your search parameters. OpenCTI search is sensitive to exact terms. Try using broader search terms or fewer parameters. |
| Connection errors | Verify that your network can reach the OpenCTI instance. Check for firewalls or network restrictions that might be blocking access. |
| Permission errors | Ensure that the API key you're using has sufficient permissions to perform the operations you're attempting. |
| Rate limiting | OpenCTI may implement rate limiting depending on your instance configuration. If you're hitting rate limits, consider implementing delays between operations. |
| Server errors (500) | These might indicate issues with your OpenCTI instance. Check the OpenCTI server logs for more information. |
Best Practices
-
Use Specific Search Terms: When possible, use specific search terms to narrow down results and improve performance.
-
Limit Result Count: Start with a smaller count value (10-25) and increase it only if needed to avoid retrieving unnecessarily large result sets.
-
Cache Results When Appropriate: If you're frequently searching for the same indicators, consider caching the results to reduce API calls to your OpenCTI instance.
-
Process Results Efficiently: The GraphQL response from OpenCTI can be complex. Use Script Nodes to extract and transform only the data you need.
-
Handle Connection Issues Gracefully: Implement error handling in your workflows to gracefully handle temporary connection issues or API errors.
-
Consider Rate Limits: Be mindful of the load your workflows place on your OpenCTI instance, especially if it's a shared resource.
-
Secure API Keys: Treat your OpenCTI API keys as sensitive credentials and use the system's built-in credential management rather than hardcoding values.
-
Update API Keys Regularly: Rotate your API keys periodically for enhanced security.
-
Monitor API Usage: Keep track of your API usage to identify inefficient workflows or potential abuse.
-
Test with Small Queries: When building new workflows, start with small, targeted searches to verify functionality before scaling up.