CrowdStrike Integration Guide
Overview
The CrowdStrike integration allows your NINA workflows to connect with CrowdStrike's Threat Intelligence and Indicators of Compromise (IOC) services. This integration enables you to create, manage, and query threat intelligence data, and to leverage CrowdStrike's powerful detection capabilities directly within your security automation workflows.
Status
The CrowdStrike API is extensive. Currently, we only support operations related to Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), which cover most of the essential functionalities for this resource. However, there are numerous other resources offered by the CrowdStrike API that we do not yet support. Some of the most significant unsupported resources include:
- Alerts: Notifications for potential security threats and incidents.
- Cloud Security Assets: Management of cloud-based security resources.
- Configuration Assessment: Evaluation of system configurations for security compliance.
- Custom IOAs: Custom Indicators of Attack for tailored threat detection.
- Detects: Detection events and alerts for suspicious activities.
- Device Control Policies: Policies for managing device access and usage.
- Event Streams: Real-time streaming of security events for monitoring.
- Falcon Intelligence Sandbox: Sandbox environment for analyzing potential threats.
- Firewall Management: Tools for configuring and managing firewall settings.
- Host Group: Grouping of hosts for streamlined management and policy application.
- Incidents: Detailed records of security incidents for investigation.
- Prevention Policy: Policies to prevent threats before they impact systems.
- Real Time Response: Immediate response capabilities for active threats.
- Spotlight Vulnerabilities: Identification and prioritization of critical vulnerabilities.
Credential Configuration
Before using the CrowdStrike integration in your workflows, you need to configure OAuth2 credentials for authentication.
Creating an API Client in CrowdStrike
- Log in to your CrowdStrike Falcon console at https://falcon.crowdstrike.com/
- Navigate to Support & Resources → API Clients & Keys
- Click Create API Client
- In the "Create New API Client" dialog:
- Enter a descriptive name for the client (e.g., "NINA Integration")
- Select Read/Write access for the following API scopes:
- IOC (Indicators of Compromise)
- IOC Exclusions
- Threat Intelligence
- Leave other options at their default settings
- Click Create
- After creation, note down the following values:
- Client ID
- Client Secret
Important: Store the Client Secret securely as it will not be displayed again.
Creating a CrowdStrike Credential in NINA
-
Navigate to the Credentials section in NINA
-
Click Add New Credential
-
Fill in the credential details:
- Name: A descriptive name (e.g., "CrowdStrike Production")
- Description: Optional details about the credential's purpose
- Integration Service: Select "CrowdStrike"
- Auth Type: "OAuth2" (only option available for CrowdStrike)
- Client ID: The Client ID from your CrowdStrike API client
- Client Secret: The Client Secret from your CrowdStrike API client
- Base URL: The CrowdStrike API endpoint for your environment
-
Click Test Connection to verify credentials
-
Click Save to store the credential
CrowdStrike API Base URLs
CrowdStrike has different base URLs depending on your environment:
| Environment | Base URL |
|---|---|
| US-1 Commercial | https://api.crowdstrike.com |
| US-2 Commercial | https://api.us-2.crowdstrike.com |
| EU Commercial | https://api.eu-1.crowdstrike.com |
| US GovCloud | https://api.laggar.gcw.crowdstrike.com |
Select the appropriate base URL for your CrowdStrike environment.
Supported Resources and Operations
The CrowdStrike integration supports the following resources and operations:
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Search Indicators | Search for indicators based on specified criteria |
| Get Indicator Details | Get details for specific indicators by their IDs |
| Create Indicator | Create a new indicator of compromise |
| Update Indicator | Update an existing indicator of compromise |
| Delete Indicator | Delete indicators by their IDs |
| Get Device Count | Get the number of devices that have observed a specific indicator |
| Get Devices Ran On | Get the IDs of devices that have observed a specific indicator |
| Get Processes Ran On | Get the processes that have been observed with a specific indicator |
| Get Combined Indicators | Get combined information for indicators including metadata |
| Aggregate Indicators | Get aggregated indicator data |
| Query IOC Types | Get a list of available IOC types |
| Query Platforms | Get a list of available platforms for indicators |
| Query Severities | Get a list of available severity levels |
| Query Actions | Search for actions that can be applied to indicators |
| Get Actions | Get details for specific actions by their IDs |
IOC Reports
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Create Indicators Report | Launch a job to create a comprehensive indicators report |
Alternate IOC Endpoints
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Devices Count | Get the number of hosts that have observed a given custom IOC |
| Devices Ran On | Find hosts that have observed a given custom IOC |
| Processes Ran On | Search for processes associated with a custom IOC |
Processes
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Get Process Details | Retrieve detailed information about specific processes |
Parameter Merging and Templating
The CrowdStrike integration takes full advantage of NINA's parameter merging and templating capabilities:
Parameter Sources (in order of precedence)
- Node Parameters: Parameters configured directly in the CrowdStrike Integration Node
- Extracted Parameters: Parameters automatically extracted from the input data
- Input Data: The complete input data from upstream nodes
When a CrowdStrike Integration Node executes:
- It combines parameters from all sources
- Node parameters take precedence over extracted parameters
- Template variables within parameters are processed (using
{{variable_name}}syntax) - The combined parameters are used to execute the CrowdStrike operation
Example: Managing Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Creating a New Indicator
Below is an example of creating a new indicator of compromise:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "create",
"parameters": {
"type": "domain",
"value": "malicious-domain.example.com",
"severity": "high",
"description": "Domain associated with Lazarus APT group campaign",
"action": "prevent",
"platforms": ["windows", "linux", "mac"],
"appliedGlobally": true,
"expiration": "2025-01-01T00:00:00Z"
}
}
Creating an Indicator with Template Variables
You can use template variables to create indicators dynamically based on input data:
Input Data from Previous Node:
{
"threat_intel": {
"ioc_type": "md5",
"ioc_value": "44d88612fea8a8f36de82e1278abb02f",
"threat_actor": "APT29",
"expiration_days": 180,
"detection_count": 15,
"malware_family": "Cozy Bear",
"source": "internal analysis",
"platform": "windows"
},
"action_required": {
"block": true
}
}
Node Configuration with Template Variables:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "create",
"parameters": {
"type": "{{threat_intel.ioc_type}}",
"value": "{{threat_intel.ioc_value}}",
"severity": "{{threat_intel.detection_count > 10 ? 'high' : 'medium'}}",
"description": "Indicator associated with {{threat_intel.threat_actor}} / {{threat_intel.malware_family}}. Source: {{threat_intel.source}}",
"action": "{{action_required.block ? 'prevent' : 'detect'}}",
"platforms": ["{{threat_intel.platform}}"],
"appliedGlobally": true
}
}
Retrieving Indicator Details
Get detailed information about specific indicators:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "get",
"parameters": {
"ids": "96afb29c561c48409e13c3d524317a9d,7a9dba78b31c4e42b9896195f33a8940"
}
}
Deleting Indicators
Remove indicators when they are no longer needed:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "delete",
"parameters": {
"ids": "96afb29c561c48409e13c3d524317a9d,7a9dba78b31c4e42b9896195f33a8940"
}
}
Example: Searching and Querying Indicators
Searching for Indicators
Search for indicators based on specific criteria:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "search",
"parameters": {
"values": ["malicious-domain.example.com", "evil-site.com"],
"types": ["domain"],
"limit": 50,
"sort": "modified_date.desc",
"additionalFields": {
"includeDeleted": false
}
}
}
Getting Combined Indicator Information
Retrieve comprehensive information about indicators with filtering:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "getCombined",
"parameters": {
"filter": "type:'domain'+severity:'high'",
"limit": 100,
"offset": 0,
"sort": "created_date|desc"
}
}
Aggregating Indicators
Perform aggregation operations on indicators:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "aggregate",
"parameters": {
"dateRange": "last_30_days",
"filter": "source:'internal'",
"fields": ["type", "severity"]
}
}
Querying IOC Types
Get a list of available indicator types:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "queryTypes",
"parameters": {
"limit": 100
}
}
Example: Device and Process Intelligence
Getting Device Count for an Indicator
Find out how many devices have observed a specific indicator:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "getDeviceCount",
"parameters": {
"type": "domain",
"value": "malicious-domain.example.com"
}
}
Getting Devices That Observed an Indicator
Retrieve the IDs of devices that have observed a specific indicator:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "getDevicesRanOn",
"parameters": {
"type": "md5",
"value": "44d88612fea8a8f36de82e1278abb02f",
"limit": 50
}
}
Getting Processes That Executed with an Indicator
Find processes that have been observed with a specific indicator:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "getProcessesRanOn",
"parameters": {
"type": "md5",
"value": "44d88612fea8a8f36de82e1278abb02f",
"limit": 50
}
}
Getting Process Details
Retrieve detailed information about specific processes:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "processes",
"operation": "getProcessDetails",
"parameters": {
"ids": "pid:123456789012:1234567890123456789,pid:987654321098:9876543210987654321"
}
}
Example: IOC Reporting
Creating a Comprehensive Indicators Report
Generate a full report of indicators matching specific criteria:
Node Configuration:
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "ioc-reports",
"operation": "createIndicatorsReport",
"parameters": {
"types": ["domain", "ip_address", "md5", "sha256"],
"format": "csv",
"additionalFields": {
"fromExpireDate": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"toExpireDate": "2025-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"source": "internal"
}
}
}
Integration in Workflow Context
The CrowdStrike integration is particularly powerful when combined with other nodes in a workflow:
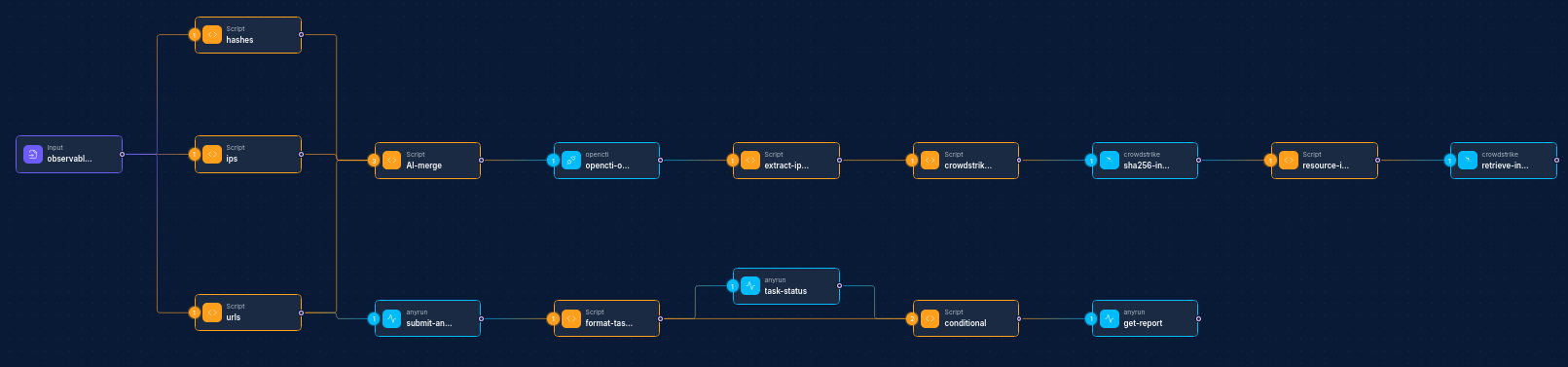
Common Workflow Patterns:
-
Threat Intelligence Enrichment:
- Input Node (IOC) → CrowdStrike Integration Node (get details) → Script Node (parse results) → Report Node
-
Indicator Management:
- Webhook Node (new IOC) → Script Node (format data) → CrowdStrike Integration Node (create indicator) → Slack Node (notification)
-
Security Alert Investigation:
- Alert Node → CrowdStrike Integration Node (search indicators) → Script Node (analyze) → CrowdStrike Integration Node (get devices) → Jira Node (ticket creation)
-
Batch IOC Processing:
- Schedule Node → File Node (read IOCs) → Script Node (parse file) → CrowdStrike Integration Node (create indicators) → Email Node (report)
-
Threat Hunting:
- Input Node (suspicious behavior) → CrowdStrike Integration Node (get process details) → Script Node (analysis) → CrowdStrike Integration Node (create IOC) → Report Node
Working with Dynamic Data
Dynamic IOC Creation from Upstream Nodes
When you have a node that produces a collection of IOCs (such as a SIEM alert or threat feed), you can dynamically create indicators in CrowdStrike:
Input Data from Previous Node:
{
"iocs": [
{
"type": "domain",
"value": "badsite1.example.com",
"severity": "high",
"confidence": 80
},
{
"type": "ip_address",
"value": "203.0.113.100",
"severity": "medium",
"confidence": 65
},
{
"type": "md5",
"value": "d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e",
"severity": "high",
"confidence": 90
}
],
"source": "external threat feed",
"tags": ["ransomware", "campaign:lockbit"]
}
Script Node (to prepare data for CrowdStrike):
// For each IOC in the input, prepare a CrowdStrike-compatible format
const crowdstrikeIocs = input.iocs.map(ioc => ({
type: ioc.type,
value: ioc.value,
severity: ioc.severity,
description: `IOC from ${input.source}. Confidence: ${ioc.confidence}%. Tags: ${input.tags.join(', ')}`,
platforms: ["windows", "mac", "linux"],
action: ioc.severity === "high" ? "prevent" : "detect",
appliedGlobally: true
}));
// Return the first IOC for immediate processing, store the rest for batch processing
return {
currentIoc: crowdstrikeIocs[0],
remainingIocs: crowdstrikeIocs.slice(1),
totalCount: crowdstrikeIocs.length
};
CrowdStrike Integration Node (with dynamic input):
{
"integration_service": "crowdstrike",
"resource": "indicators",
"operation": "create",
"parameters": {
"type": "{{currentIoc.type}}",
"value": "{{currentIoc.value}}",
"severity": "{{currentIoc.severity}}",
"description": "{{currentIoc.description}}",
"action": "{{currentIoc.action}}",
"platforms": "{{currentIoc.platforms}}",
"appliedGlobally": "{{currentIoc.appliedGlobally}}"
}
}
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Resolution |
|---|---|
| Authentication failures | Verify your API client credentials and ensure your client has the necessary scopes enabled. |
| "Access Denied" errors | Check that your API client has the appropriate WRITE permissions for the endpoint you're using. |
| Rate limiting | CrowdStrike enforces rate limits. If you hit these limits, implement exponential backoff in your workflows. |
| Invalid IOC format | Ensure your indicator values match the expected format for the type (e.g., valid domain names, properly formatted hashes). |
| Expired API tokens | The integration automatically handles token refresh. If persistent issues occur, recreate your API client. |
| Missing indicators | Check if indicators were created with an expiration date that has passed or if they were deleted. |
| Indicator creation fails | Verify that the combination of type and value is valid and not already present in your CrowdStrike environment. |
| Missing device data | Ensure the sensor is installed and active on the devices you're querying. |
| Insufficient permissions | Verify your API client has the necessary role-based permissions in your CrowdStrike tenant. |
| Report generation timeout | Reports for large datasets may time out. Consider filtering your report parameters or processing data in batches. |
Best Practices
-
Scope API Tokens Properly: Give your API client only the permissions it needs for the operations you'll perform.
-
Manage Indicator Expiration: Set appropriate expiration dates for indicators to avoid cluttering your CrowdStrike environment.
-
Use Descriptive Descriptions: Include source information, confidence levels, and context in your indicator descriptions.
-
Apply Targeted Actions: Use the "prevent" action judiciously, especially for indicators that might cause false positives.
-
Leverage Template Variables: Use NINA's template variables to create dynamic, context-aware indicators.
-
Batch Process When Possible: When creating multiple indicators, use batch processing to reduce API calls and improve performance.
-
Implement Error Handling: Add error handling for rate limiting, authentication issues, and other potential API problems.
-
Document Custom Indicators: Maintain documentation for custom indicators created through the integration.
-
Regularly Audit Indicators: Periodically review and clean up indicators that are no longer relevant.
-
Consider Performance Impact: Be mindful of the potential performance impact when applying new prevention-based indicators across your environment.