NINA User Guide
Introduction
NINA is a sophisticated workflow orchestration platform designed to execute security tools in a distributed manner. This guide will help you understand the core concepts and how to effectively use the platform.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Workflows
- Working with Nodes
- Creating Connections with Edges
- Executing Workflows
- Managing Workflow Executions
- Working with Tools
- Integration Capabilities
- Advanced Features
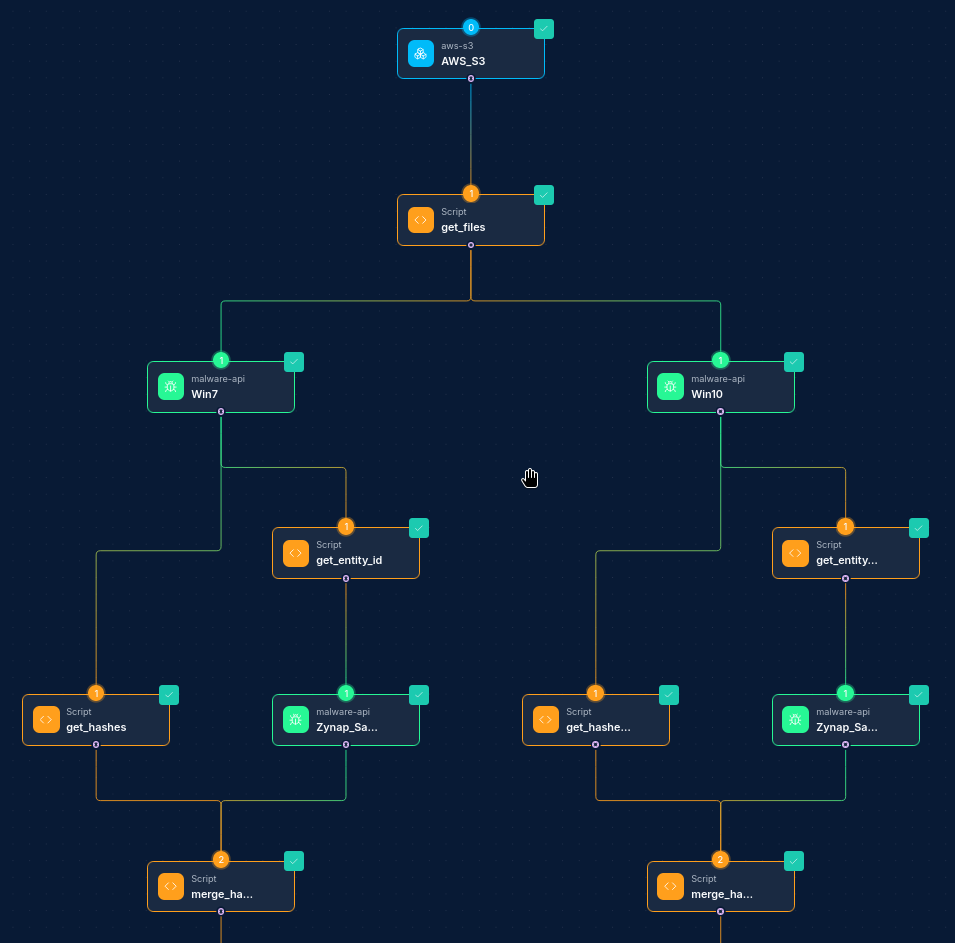
Understanding Workflows
A workflow in NINA is a directed acyclic graph (DAG) that represents a sequence of operations to be performed. Workflows consist of nodes (operations) connected by edges (relationships between operations).
Key Workflow Concepts
- Workflow Definition: A reusable template that defines a set of operations and their connections
- Workflow Execution: A specific instance of a workflow being run with its own execution state
- Nodes: Individual operations within a workflow (inputs, processing steps, outputs)
- Edges: Connections between nodes that define the flow of data and execution order
- Branches: Parallel execution paths within a workflow
Workflow States
Workflows can exist in various states during execution:
- Pending: Workflow is initialized but not yet running
- Running: Workflow is actively executing nodes
- Held: Workflow execution is paused (manually or due to conditions)
- Complete: All nodes have successfully completed execution
- Failed: One or more nodes have failed, halting the workflow
- Partially Complete: Some branches have completed while others have failed or are held
Working with Nodes
Nodes are the building blocks of workflows, representing individual operations or processing steps.
Node Types
NINA supports several specialized node types:
- Input Node: Provides initial data to the workflow (text values, files)
- Operation Node: Executes a specific security tool with configured parameters
- Script Node: Runs custom code (Python, Bash, AI prompt) for data transformation or analysis
- API Node: Interacts with external APIs or services
- Integration Node: Connects with third-party platforms or Zynap's internal services using predefined integrations
- Hacking Node: Specialized node for security operations
- Compromised Machine Node: Special type of node that would appear if a Hacking Node has an attachable target
Node States
During workflow execution, nodes progress through several states:
- Pending: Node is waiting for dependencies to complete
- Running: Node is actively executing
- Complete: Node has successfully finished execution
- Failed: Node encountered an error during execution
- Held: Node execution is paused (manually or conditionally)
Adding Nodes
To add nodes, simply drag and drop a node type from the available nodes.
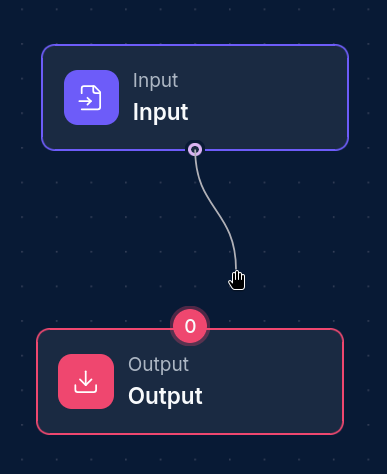
Creating Connections between Nodes
"Edges" aka Connections, define the relationships between nodes, controlling data flow and execution order.
Edge Properties
- From/To Nodes: Specifies the source and destination nodes
- Branch Flag: This is enabled whenever a node has connections to more than 1 downstream node
Creating Edges
- Select the source node (where data comes from)
- Select the destination node (where data goes to)
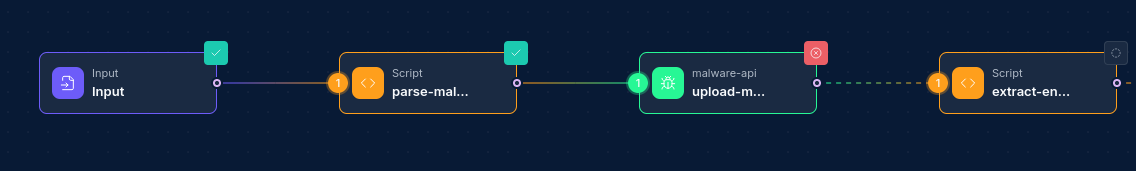
Executing Workflows
Executing a workflow processes all nodes in the correct order based on their dependencies.
Execution Process
- The workflow engine builds an execution graph from the workflow definition
- Root nodes (those with no dependencies) begin execution first
- As nodes complete, their downstream dependencies are checked
- Nodes with satisfied dependencies are executed in parallel when possible
- Execution continues until all nodes complete or an error occurs
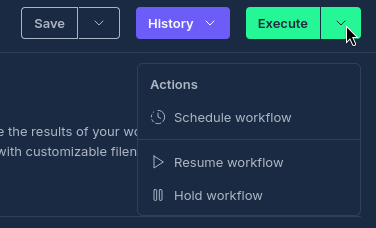
Execution Controls
- Start: Begin workflow execution from the beginning
- Stop: Halt a running workflow (gracefully terminates all running nodes)
- Hold: Pause workflow execution at the current point or after specific nodes
- Resume: Continue execution of a held workflow
- Execute From Node: Restart execution from a specific node, preserving previous results
Managing Workflow Executions
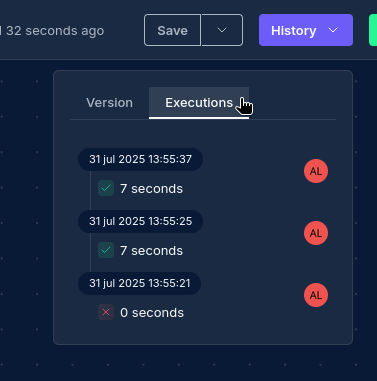
Each time a workflow is executed, a new workflow execution is created with its own state and history.
Execution History
The execution history provides details about:
- When the workflow started and completed
- The status of each node execution
- Any errors that occurred during execution
- The outputs produced by each node
Viewing Node Results
For each node execution, you can:
- View a truncated version of the output data in the bottom view
- Download result files using the "Download" button to retrieve the full data file
- See execution timing information
- Review any errors or warnings
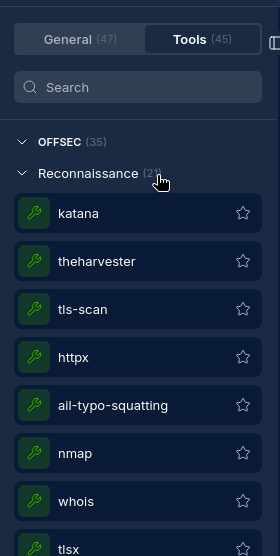
Working with Tools
NINA includes a registry of security tools that can be used in Operation Nodes. Every tool is considered an Operation Node.
Available Tools
The platform includes various security tools for:
- Subdomain discovery
- Port scanning
- Vulnerability scanning
- Web crawling
- And more...
Tool Configuration
Each tool has:
- Required and optional parameters
- Supported input and output formats
- TO BE ADDED: Documentation on usage and examples
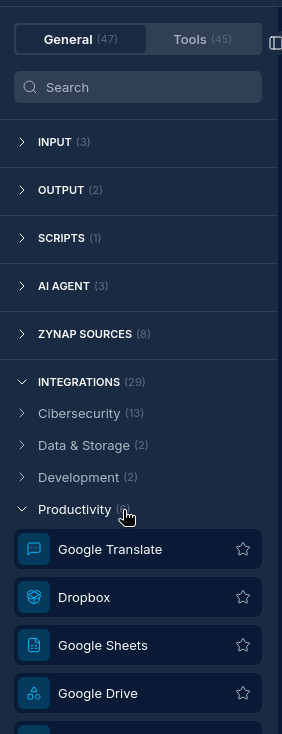
Integration Capabilities
NINA can integrate with external services and platforms through dedicated integration nodes.
Supported Integrations
- Slack: Send notifications and results to Slack channels
- Jira: Create and update tickets based on workflow results
- OpenCTI: Interact with threat intelligence platforms
- CrowdStrike: Connect to security platforms
- Outlook: Email capabilities for notifications and data collection
- Custom API: Connect to any REST API with configurable parameters
Advanced Features
Branching and Parallel Execution
Create complex workflows with parallel processing branches:
- Execute multiple tools against the same target simultaneously
- Process different aspects of results in parallel
- Merge results from multiple paths at convergence points
Workflow Templates
Save and reuse common workflow patterns:
- Security scanning templates
- Reconnaissance workflows
- Reporting templates
- Custom analysis pipelines
Scheduling
Schedule workflows to run automatically:
- One-time future execution
- Recurring executions on a schedule
- Conditional execution based on triggers