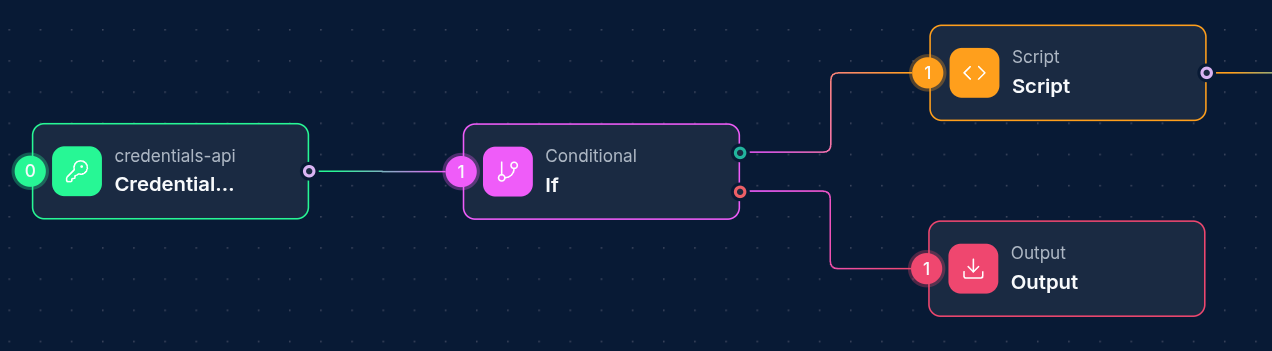
IF Node Guide
Overview
The IF Node is a conditional control flow component that enables dynamic branching in your workflows based on data evaluation. It assesses conditions against input data and determines which path the workflow should follow next, allowing for sophisticated decision-making capabilities within your automation processes.
Use Cases
- Implementing business logic rules (e.g., determining eligibility based on multiple criteria)
- Filtering data based on specific attributes
- Creating conditional notification paths (e.g., alert only for high-severity findings)
- Implementing feature flags and conditional functionality
- Validating input data before proceeding with processing
- Creating different processing branches based on data characteristics
- Implementing complex multi-step decision trees
Creating an IF Node
Basic Setup
- Drag an IF Node from the node palette onto your workflow canvas
- Connect it to one or more input nodes that provide the data to evaluate
- Configure condition groups and the combine operator
- Create outgoing connections with appropriate edge types (true/false) to downstream nodes
Condition Configuration
Configuring an IF node involves setting up conditions that will be evaluated against incoming data:
- In the node configuration panel, add one or more condition groups
- For each group, set the logical operator (AND/OR) to combine conditions within the group
- Add individual conditions to each group
- Set the top-level combine operator to determine how group results are combined
- Connect true/false edges to appropriate downstream nodes
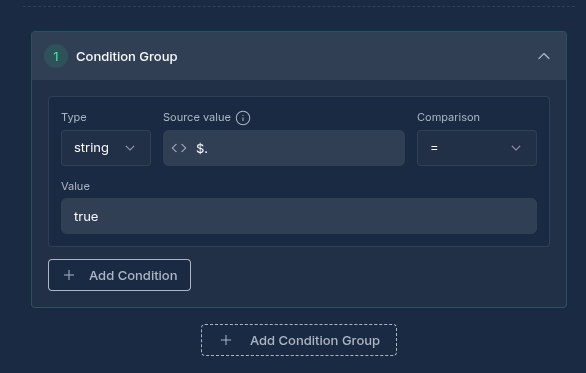
Configuration Options
Node Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | A descriptive name for the node |
| Input Type | The type of input data (usually "json") |
| Output Type | The type of output data (usually "json") |
| Condition Groups | Groups of conditions to evaluate |
| Combine Operator | Logical operator (AND/OR) to combine group results |
Condition Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Left Value | JSONPath expression or value to evaluate (e.g., $.user.age) |
| Comparison Type | Type of comparison (equals, not_equals, contains, etc.) |
| Right Value | Value or JSONPath expression to compare against |
| Value Type | Data type for comparison (string, number, boolean) |
Supported Comparison Types
The IF node supports these comparison types:
| Comparison | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Equals | Checks if values are equal | $.status = "active" |
| Not Equals | Checks if values are not equal | $.status != "inactive" |
| Contains | Checks if a string contains another string | $.email contains "@company.com" |
| Greater Than | Checks if left value is greater than right value | $.age > 18 |
| Less Than | Checks if left value is less than right value | $.score < 100 |
| Regex | Checks if left value matches a regex pattern | $.email matches "^.+@gmail\.com$" |
| Empty | Checks if a value is empty (null/empty string/array/object) | $.tags is empty |
| Not Empty | Checks if a value is not empty | $.tags is not empty |
Condition Grouping
The IF node supports a hierarchical condition structure with two levels of logical operations:
Group Level
- Multiple conditions within a group are combined using the group's operator (AND/OR)
- Use AND when all conditions must be true
- Use OR when any condition can be true
Node Level
- Multiple condition groups are combined using the top-level combine operator (AND/OR)
- Use AND when all groups must evaluate to true
- Use OR when any group can evaluate to true
How IF Nodes Work
When a workflow is executed:
- The IF Node receives input data from upstream nodes
- JSONPath expressions in conditions are resolved against the input data
- Each condition is evaluated based on its comparison type and resolved values
- Condition results are combined using the group operator (AND/OR)
- Group results are combined using the combine operator (AND/OR)
- The final boolean result (true/false) determines which branch to follow
- The node writes detailed evaluation results to its output
- Downstream nodes connected with the appropriate edge type (true/false) are executed
Evaluation Process Diagram
sequenceDiagram
participant Input as Input Data
participant IF as IF Node
participant True as True Branch
participant False as False Branch
Input->>IF: Provide data
IF->>IF: Evaluate conditions
IF->>IF: Combine results
alt Condition Result = True
IF->>True: Execute true branch
else Condition Result = False
IF->>False: Execute false branch
end
JSONPath Usage
The IF node uses JSONPath expressions to access data within the input JSON:
- Basic property access:
$.user.name - Array indexing:
$.items[0].value - Multiple levels:
$.data.users[0].profile.settings.notifications
Examples of JSONPath Expressions
$.customer.age // Access a simple property
$.orders[0].total // Access the first item in an array
$.products[*].price // Use wildcard to access all prices (returns array)
$.user.profile.address.city // Access deeply nested properties
Best Practices
Condition Design
-
Order Conditions Efficiently:
- Put low-cost conditions first in AND groups
- Put high-probability conditions first in OR groups
-
Use Appropriate Value Types:
- Specify
value_typeas "string", "number", or "boolean" - This ensures proper comparison semantics
- Specify
-
Handle Missing Data:
- Use the
emptyandnot_emptycomparison types to check existence - Add validation conditions before accessing nested properties
- Use the
Condition Grouping
-
Logical Organization:
- Group related conditions that naturally belong together
- Use AND for conditions that all must be true together
- Use OR for alternative conditions
-
Complex Logic Implementation:
- To implement "A AND (B OR C)":
- Create a group for A with AND operator
- Create another group for B and C with OR operator
- Use AND as the combine operator
- To implement "(A AND B) OR (C AND D)":
- Create a group for A and B with AND operator
- Create another group for C and D with AND operator
- Use OR as the combine operator
- To implement "A AND (B OR C)":
Example Configurations
Example 1: Simple Age Verification
Evaluates if a user is over 18 years old.
{
"condition_groups": [
{
"id": "group1",
"conditions": [
{
"id": "condition1",
"left_value": "$.user.age",
"comparison_type": "greater_than",
"right_value": "18",
"value_type": "number"
}
],
"operator": "and"
}
],
"combine_operator": "and"
}
Input Data:
{
"user": {
"id": 12345,
"name": "John Doe",
"age": 25,
"email": "[email protected]"
}
}
Example 2: Premium Customer Qualification
This example checks if a customer is premium either by:
- Having total purchases > $1000 AND account age > 365 days, OR
- Having "platinum" VIP status
{
"condition_groups": [
{
"id": "group1",
"operator": "and",
"conditions": [
{
"id": "cond1",
"left_value": "$.customer.totalPurchases",
"comparison_type": "greater_than",
"right_value": "1000",
"value_type": "number"
},
{
"id": "cond2",
"left_value": "$.customer.accountAge",
"comparison_type": "greater_than",
"right_value": "365",
"value_type": "number"
}
]
},
{
"id": "group2",
"operator": "and",
"conditions": [
{
"id": "cond3",
"left_value": "$.customer.vipStatus",
"comparison_type": "equals",
"right_value": "platinum",
"value_type": "string"
}
]
}
],
"combine_operator": "or"
}
Example 3: Input Validation
Checks if essential data is present before processing:
{
"condition_groups": [
{
"id": "validation",
"operator": "and",
"conditions": [
{
"id": "check1",
"left_value": "$.apiKey",
"comparison_type": "not_empty"
},
{
"id": "check2",
"left_value": "$.target",
"comparison_type": "not_empty"
},
{
"id": "check3",
"left_value": "$.options",
"comparison_type": "not_empty"
}
]
}
],
"combine_operator": "and"
}
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Resolution |
|---|---|
| Condition not evaluating as expected | Check the value types and ensure proper comparison type is used |
| JSONPath not resolving | Verify the path exists in your input data and check for typos |
| Missing fields | Verify upstream nodes are providing the expected data structure |
| Type conversion failures | Check if the data matches the specified value type |
Working with Edge Types
The IF node relies on edge types to determine which downstream nodes should execute:
Edge Types for IF Nodes
- True Edge: Connect this edge to nodes that should execute when the condition is true
- False Edge: Connect this edge to nodes that should execute when the condition is false
To configure an edge type, create a connection from the IF node's true/false edge to a downstream node
Next Steps
After configuring your IF Node, you might want to:
- Add different processing nodes in the true/false branches
- Chain multiple IF nodes for complex decision trees
- Use Script nodes to prepare data for condition evaluation